Deformation of the arthrosis of the knee joint is a polyetological disease. This means there are many reasons for its development. In some cases, when the most predominant cause can be separated, gonarthrosis is called secondary. In the case where a clear cause is not determined, the diagnosis of primary or idiopathic arthrosis of the knee joint is established.

Normally, the destruction of the joint cartilage occurs in the process of physiological whitening of the whole organism, that is, during aging. The pathological destruction of the cartilage is considered when it occurs prematurely or more intense rhythm. The average age, in which on a fully legitimate basis, the first signs of cartilage degeneration can manifest itself is a period of 40 to 50 years. With arthrosis deformity, the disease debuts in childhood with the first manifestations of 16 - 18 years, and in some cases even earlier. However, this is not a reason to despair.
The mechanism of developing the disease is a wicked circle in which final connections begin the beginner and so on infinity. However, every round of this circle exacerbates the condition of the cartilage and leads to the progression of the disease, etc. In the case of primary gonartrosis, the reason that begins a bad circle is unknown. However, its subsequent connections are carefully studied with the aim of influencing them and slowing the progression of the disease.
Arthrosis deformity develops approximately as follows. The daily joint cartilage of the common knee joint experiences thousands of strokes that are forced to depreciate so as not to harm the tender structures of the human body, such as the internal organs and the brain. Over time, due to shock data, microscopic cracks are formed in the cloudy layer, which are also filled with synovial fluid and turned into microdists after a certain period of time. Neighboring microdists have a tendency to unite and form larger cysts.
Growing to the size of the corneal space cysts gradually begin to squeeze the blood capillaries that feed the cartilage tissue from the bone. Its oxygen supply and substances needed to maintain life activity deteriorates, which leads to a slower synthesis of type 2 collagen.
The cartilage carriage leads to two negative consequences. First, it leads to a deterioration in the properties of depreciation and a more intense formation of new micrococks in the subsidiary layer. Second, due to the compression of the cartilage, its density increases, which adversely affects the second mechanism of its food-through the distribution of synovial fluid in the thickness of the cartilage tissue.
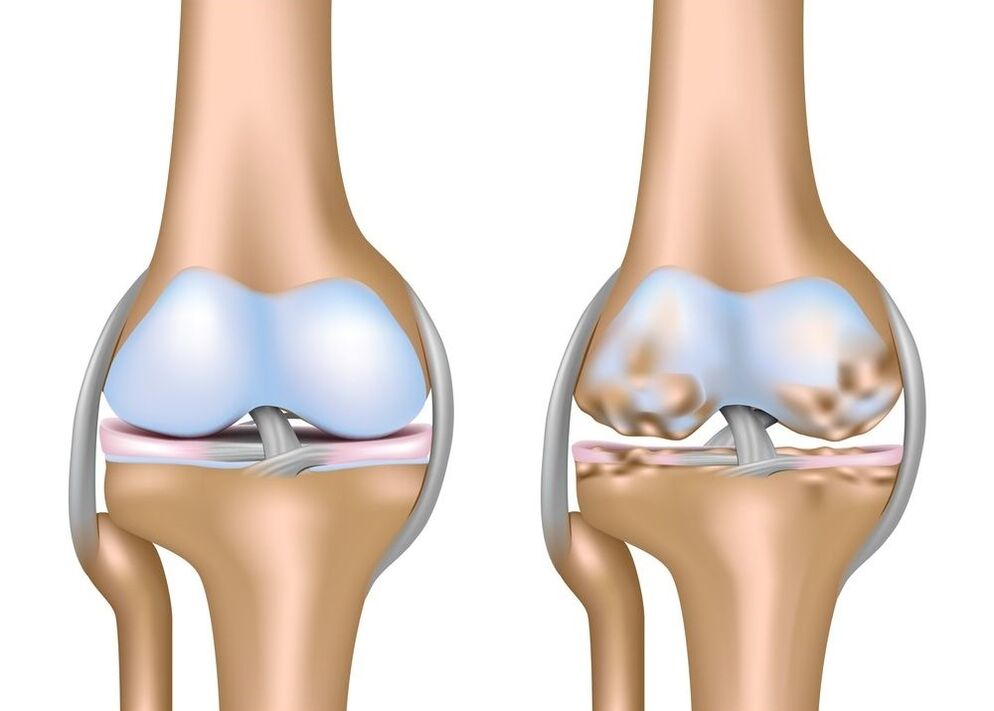
However, at the scale of the whole organism, the destruction of the articular cartilage does not pass unnoticed. As a compensatory reaction to the focus of the washing cartilage, the activity of the chondroblasts - new cells that synthesize new cartilage tissue increases. However, this compensatory mechanism is imperfect, and its imperfection lies in the fact that most of the cartilage tissue is formed not at the site of greater cartilage destruction, but where the cartilage does not experience loads.
As a result, the increase in the cartilage of the cone -shaped cartilage are formed along the edges of the joint condroofites. These condroofites do not clinically manifest until ossification processes begin. Okreteen, condroofites harden and turn into, which are called spikes in ordinary people. As a rule, the appearance of points is always associated with the appearance of pain and the development of inflammation in the joint. This is due to the fact that osteophytes during joint movement affect the cartilage tissue and synovial shell, mechanically damaging it.
As a result, any complication of deformation arthrosis leads to the acceleration of the progress of pathological changes in the cartilage. However, recognizing the mechanism of gonartrosis development can successfully affect some of its connections in order to slow its current and improve a long -term forecast.
Secondary gonartrosis differs from the main one to what is known the main reason, which began a wicked circle of destruction of the joint. The further course of the disease appears in the same way as with primary gonarthrosis, with the uniqueness that the disease is constantly exacerbated by the effect of negative factors associated with the underlying disease. For this reason, the secondary arthrosis course of the knee joint, as a rule, is more aggressive.
Post -traumatic deformation arthritis is divided into acute and chronic. The acute form of the disease develops after serious injury, most often -
, which occurs or partially extends to the articular part of the bone. The chronic form of the disease develops for a longer time and is associated, as a rule, with frequent and minor damage to the joint. Such conditions are created by builders, road workers, motors, etc.
In acute gonartrosis, the mechanism of the disease is associated with severe inflammatory changes in the joint cavity, namely lymphostasis, increased pressure in the joint cavity, and a change in the composition of synovial fluid. Excessive acceleration of the growth of the new cartilage fabric leads to deformation of the articular surface at the fracture site and the growth of osteophytes.
In chronic gonartrosis, a severe inflammatory process is not observed, however, frequent and intense load on the cartilage tissue leads to its rapid compression, microcock formation, and deteriorating the supply of nutrients by both the bone and the joint gap.
People with this pathology can be found quite often. Its essence is to change the shape of the legs. With variable deformation, the legs are arched externally on a horizontal plane. In other words, among the patient's feet, space is more than in healthy people. With valgus deformation, the legs have an X-shaped shape when the knees are in contact with each other. Both pathologies can be genetically programmed and develop throughout life due to fractures of the lower extremities.
In both cases, the load on one of the sides of the knee joint increases, with varus deformation - on the sides, and with valgus deformity - on the medial sides. Due to the fact that the same weight of the patient suppresses in a smaller area, premature cartilage occurs, accompanied by inflammation, pain and morning stiffness.
Congenital shortening of one of the legs is a consequence of abnormalities or may develop several years after birth as a result of birth damage. As in the previous case, an uneven weight distribution occurs, and the normal leg takes a large load. As a result, the joint cartilage of the knee joint of a healthy foot undergoes structural changes that lead to arthrosis deformity.
This pathological condition is not a disease, but it can lead to it. This syndrome implies excessive mobility of the ligamentous and stable apparatus, in which the joint movement of the joints within normal axes can increase significantly. Such patients almost never suspect that they have such a feature, as they live with their entire lives and believe that other people also work the same way.
A sign of the knee joint hypersmower is the formation of a stupid angle between the front surfaces of the thigh and the lower leg with the maximum direction of the foot. In other words, the knees are bending the way they were, and the legs get a fiery shape. Also, such patients can easily reach the forearm with the thumb, reach their heads on their feet and, in principle, have congenital flexibility.
The symptoms of arthrosis of the knee joint
In the initial stage of development, the pathology is manifested by knee pain, moderately expressed and arising in motion when moving along the steps.
An unpleasant symptom can appear if a person spends a lot of time standing or tries to get up after being in a sitting position for a long time.
At rest, health usually improves.
Severe severe severe pain arises spontaneously.
Most patients previously had prolonged discomfort during physical activity and when walking. In this case, increased pain can be the main sign of gonarthrosis development.
The disease develops gradually, for several months or years, when it is not yet significant deformity and severe pain. But during this period, knee discomfort, which occurs occasionally.
Remember, the earlier you consult a doctor, the easier and successfully the treatment will pass.
Do not delay a visit to a specialist, waiting for irreversible consequences. Take action as soon as you notice the symptoms of the disease.
Visible signs of knee joint arthrosis begin to manifest as the structure of cartilage shells, a decrease in the production of synovial fluid and damage to the joint bag. In the initial phase of increasing pathological changes, as a rule, there are no pronounced symptoms, but at the same time a slight stiffness may be present in the morning.
When pronounced and various symptoms appear, arthritis, as a rule, is already in the late stage of their development. At this time, there is already serious damage to the knee joint structures, so the disease goes to the acute phase. Characteristic manifestations of the acute period of arthritis development include:
When knee arthritis develops, the symptoms can grow long enough, but when the disease is going through the last 3 phase of the onset of a joint disorder, the quality of life significantly reduces the quality of life.
In the development of a condition such as knee arthrosis, symptoms and treatment are interconnected, since if in the early stages of development of the disease, articular surfaces can still be fully restored and improved by local metabolism, then in the later stages the treatment of arthrosis of the knee can often have a positive effect, sinceare expressed.
The 1st degree arthrosis persists almost without apparent symptoms. This stage of development is characterized by:
Symptoms of pain, if and occur, manifest to a small degree. At the moment, knee arthritis looks at X -Ray in the form of small bumps in the cartilage tissue and bone surface.
With the arthrosis of the knee joint of the 2nd degree, the symptoms are more pronounced. Pain already arises from the minimum load or immediately after it. In the affected part of the foot, the pain is caused by almost any movement. After a fairly long break, it usually passes completely. However, the other physical actions immediately cause pain.
In the second phase of the development of the disease, pain sensations increase:
A rough crisis of arthrosis joints, as a rule, is first barely obedient, but with the course of the disease becomes very noisy and special. When you try to bend your leg to the knee, a sharp pain occurs. In some cases, this is only possible for a corner of 90 degrees, and then with difficulty and overcoming pain. The change in the form of fusion also becomes apparent, which is also exacerbated by the accumulation of pathological fluid in it.
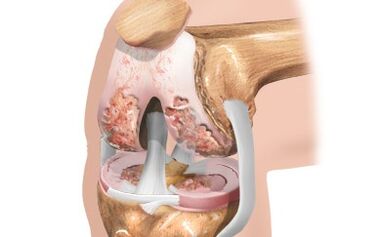
The characteristic features of the 3rd degree of arthrosis are severe pain that is independent of the quantity, the intensity of physical activity. The summary concerns a person even at night, this causes considerable concerns.
Radiography can indicate global changes in cartilage, joint surface, non -characteristic growth. O or X -shaped curvature leads a person to disability. These are the consequences that the cartilage tissue has already tired and bone tissue has entered the "movement".
Gonartrosis is a degenerative-destrophic disease, in which the destruction of the cartilage occurs and the knot is deformed. Signs of the disease are severe pain, limb deformity, an uneven distribution of load on the bone-muscular system, developing complications, and a significant decrease in mobility to the patient's disability.



















